EU’s EV & Battery Trade Policy: Where To Next?
Introduction
The European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of the electric vehicle (EV) and battery revolution, setting ambitious targets for a sustainable and low-carbon economy. To achieve these goals, the EU has been actively promoting trade policies that support the development and growth of the EV and battery industries. This article explores the current state of EU’s EV and battery trade policy and discusses the direction it might take in the future.
Current Situation
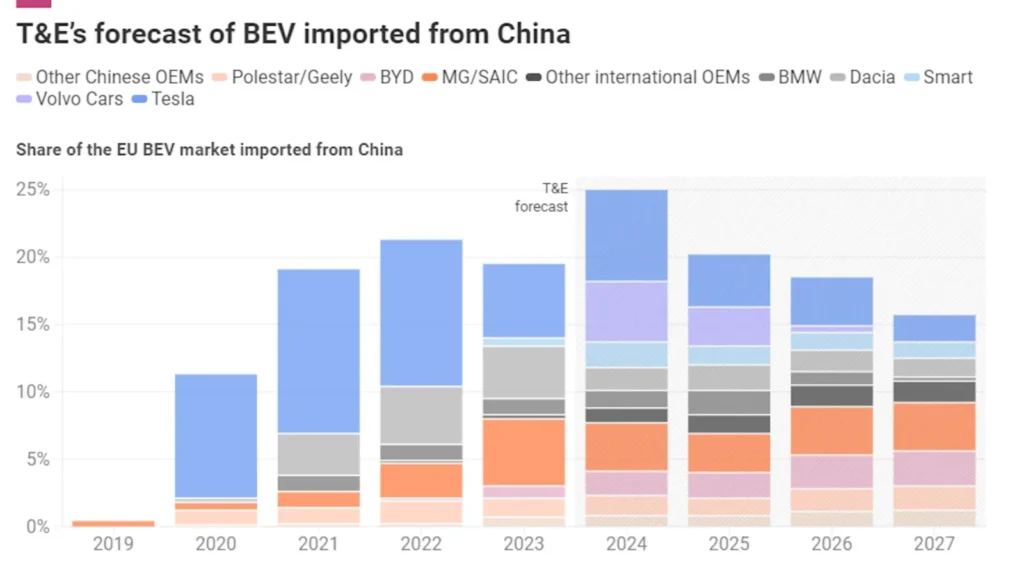
The EU has implemented several trade measures to promote the growth of the EV and battery industries. For instance, the EU has imposed anti-dumping duties on imports of certain EV batteries from countries such as China, Korea, and Japan. This move aims to protect domestic producers from unfair competition and to ensure a level playing field.
The EU has also been actively promoting the development of the EV battery value chain through its investment in research and development (R&D) initiatives. The European Commission has committed to investing €10 billion in R&D projects aimed at developing sustainable batteries and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Future Directions
So, where does the EU’s EV and battery trade policy go from here? There are several potential directions that the EU could take:
Strengthening Trade Enforcement
The EU could strengthen its trade enforcement mechanisms to ensure that companies comply with trade agreements and regulations. This could include increasing resources for customs enforcement and enhancing cooperation with other countries to combat trade evasion.
Promoting Sustainable Trade
The EU could promote sustainable trade practices by incorporating environmental and social criteria into its trade agreements. This could include requirements for companies to meet certain standards for labor rights, human rights, and environmental protection.
Encouraging Investment in R&D
The EU could encourage investment in R&D initiatives that support the development of sustainable batteries and EV technologies. This could include providing financial incentives, tax breaks, and other forms of support to companies that invest in R&D.
Diversifying Supply Chains
The EU could diversify its supply chains by investing in new technologies and companies that are not reliant on traditional suppliers. This could include investing in companies that use alternative materials, such as graphene or sodium-ion batteries.
Building International Cooperation
The EU could build international cooperation with other countries to promote the development of sustainable batteries and EV technologies. This could include collaborating with countries to share knowledge, expertise, and resources, and to develop common standards and regulations.
Conclusion
The EU’s EV and battery trade policy has been an important driver of innovation and growth in the industry. To continue driving progress, the EU should consider strengthening trade enforcement, promoting sustainable trade practices, encouraging investment in R&D, diversifying supply chains, and building international cooperation.
FAQs
Q: What is the EU’s target for electric vehicle adoption?
A: The EU aims to have at least 50% of new car sales be electric by 2035.
Q: What is the EU’s strategy for promoting the development of sustainable batteries?
A: The EU has committed to investing €10 billion in R&D initiatives aimed at developing sustainable batteries and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Q: How does the EU plan to address trade competition from other countries?
A: The EU has imposed anti-dumping duties on imports of certain EV batteries from countries such as China, Korea, and Japan to protect domestic producers from unfair competition.
Q: Will the EU’s EV and battery trade policy impact international trade agreements?
A: Yes, the EU’s EV and battery trade policy is likely to impact international trade agreements, particularly in the context of the ongoing negotiations on the EU-US trade agreement.



_2.png?w=150&resize=150,150&ssl=1)


