The Rise of Renewable Energy
The world is undergoing a significant transformation in the way we generate and consume energy. The increasing awareness of climate change, the depletion of fossil fuels, and the need for sustainable development have led to a surge in the adoption of renewable energy sources. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy accounted for 26% of global electricity generation in 2020, up from 21% in 2010.
Key Players in the Renewable Energy Landscape
Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power are gaining traction globally. Solar energy has emerged as a leading player, with over 720 gigawatts (GW) of installed capacity worldwide. Wind power is another significant contributor, with over 540 GW of installed capacity. Hydroelectric power remains a reliable source, with over 1,200 GW of installed capacity.
The Power of Power Engineering in Renewable Energy
Power engineering plays a crucial role in the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid. The goal is to ensure a stable, efficient, and reliable supply of electricity. Power engineers must design and develop systems that can efficiently transmit and distribute energy generated from renewable sources. This requires a deep understanding of power electronics, electrical systems, and control systems.
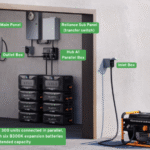
Grid-Scale Energy Storage
Grid-scale energy storage is a critical component in the integration of renewable energy sources. Power engineers must design and develop energy storage systems that can store excess energy generated from solar panels or wind turbines during periods of low demand. This stored energy can then be released during peak demand periods, ensuring a stable electricity supply.
The Synergy Between Power Engineering and Renewable Energy
The synergy between power engineering and renewable energy is evident in the development of innovative solutions that address the challenges of integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. For example, power engineers have developed advanced power converters that can efficiently convert DC power from solar panels or wind turbines to AC power for distribution to consumers.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the synergy between power engineering and renewable energy offers significant opportunities, there are challenges to be addressed. Power engineers must balance the variability of renewable energy sources with the need for a stable and reliable electricity supply. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources requires significant investment in infrastructure, including transmission and distribution lines, substations, and energy storage facilities.
Conclusion
The synergy between power engineering and renewable energy is a recipe for sustainability. As the world transitions to a low-carbon economy, power engineers will play a critical role in the design and development of innovative solutions that address the challenges of integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. By combining expertise in power engineering with the power of renewable energy, we can create a more sustainable, efficient, and reliable energy system for the future.
FAQs
Q: What are the most common sources of renewable energy?
A: Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power are the most common sources of renewable energy.
Q: What is the role of power engineering in renewable energy?
A: Power engineering plays a crucial role in the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid, ensuring a stable, efficient, and reliable supply of electricity.
Q: What is grid-scale energy storage?
A: Grid-scale energy storage refers to the storage of excess energy generated from renewable sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, for release during peak demand periods.
Q: What are the challenges of integrating renewable energy sources into the grid?
A: Power engineers must balance the variability of renewable energy sources with the need for a stable and reliable electricity supply, and invest in infrastructure, including transmission and distribution lines, substations, and energy storage facilities.

_1.png?w=150&resize=150,150&ssl=1)


(1).png?w=150&resize=150,150&ssl=1)
