What is Energy Storage?
Energy storage is the process of storing energy for later use. This can be done through various methods, including mechanical, thermal, and electrochemical means. Energy storage is an important part of our energy system, as it allows us to regulate the flow of energy from generation to consumption, providing stability and reliability to the grid.
Types of Energy Storage
1. Pumped Hydro Storage (PHS)
Pumped hydro storage is the most widely used form of energy storage globally. It involves pumping water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir during off-peak hours when electricity is plentiful, and then releasing it through a turbine to generate electricity during peak hours.
2. Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) use rechargeable batteries to store excess energy generated by renewable sources, such as solar or wind power. BESS can provide power during periods of low renewable energy production, improving grid stability and reliability.
3. Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) involves compressing air in an underground cavern during off-peak hours, and then releasing it through a turbine to generate electricity during peak hours. CAES is a flexible and cost-effective form of energy storage.
4. Flywheel Energy Storage (FES)
Flywheel energy storage (FES) uses mechanical flywheels to store energy. During periods of excess energy production, the flywheel is charged by converting the excess energy into mechanical energy. The flywheel then releases this energy back into the grid during periods of high demand.
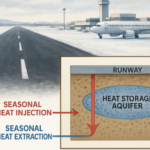
5. Thermal Energy Storage (TES)
Thermal energy storage (TES) involves storing thermal energy in the form of hot or cold media, which can be used to generate electricity or provide heating or cooling. TES is particularly useful for renewable energy sources, such as concentrated solar power.
Benefits of Energy Storage
Improved Grid Reliability
Energy storage helps to stabilize the grid by regulating the flow of energy between generation and consumption. This reduces the likelihood of blackouts and improves overall grid reliability.
Renewable Energy Integration
Energy storage enables the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid. By storing excess energy generated during periods of high production, energy storage helps to provide a stable supply of energy during periods of low production.
Peak Shaving
Energy storage helps to reduce peak demand during periods of high energy consumption, such as summer afternoons. This reduces the strain on the grid and prevents brownouts and blackouts.
Applications of Energy Storage
Grid-Scale Energy Storage
Grid-scale energy storage involves the deployment of energy storage systems on a large scale to provide grid stability and reliability. This can include the integration of renewable energy sources and the management of peak demand.
Microgrid Energy Storage
Microgrid energy storage involves the deployment of energy storage systems at the local level, typically for remote communities or buildings. This provides a reliable and sustainable source of energy.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Energy Storage
V2G energy storage involves the use of electric vehicles as energy storage devices. During periods of low energy demand, vehicles can store excess energy and then supply it back to the grid during periods of high demand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, energy storage is a crucial component of our energy system, providing stability, reliability, and flexibility to the grid. The various types of energy storage, including pumped hydro storage, battery energy storage systems, compressed air energy storage, flywheel energy storage, and thermal energy storage, offer a range of benefits and applications. As the world transitions to a more renewable energy-based grid, the importance of energy storage will only continue to grow.
FAQs
Q: What is the most widely used form of energy storage?
A: Pumped hydro storage is the most widely used form of energy storage globally.
Q: What are the benefits of energy storage?
A: Energy storage improves grid reliability, enables the integration of renewable energy sources, and reduces peak demand.
Q: What are the different types of energy storage?
A: There are several types of energy storage, including pumped hydro storage, battery energy storage systems, compressed air energy storage, flywheel energy storage, and thermal energy storage.
Q: What is V2G energy storage?
A: V2G energy storage involves the use of electric vehicles as energy storage devices, allowing them to supply excess energy back to the grid during periods of high demand.



.png?w=150&resize=150,150&ssl=1)
.png?w=150&resize=150,150&ssl=1)

